The economic crisis of Sri Lanka in 2022 had a severe and alarming impact on the nation. In 2023, its GDP dropped drastically. During this period, the government implemented robust stabilization measures to tackle this problem.
In spite of these efforts, its IMF review was unsuccessful due to gripping debt burden and low-GDP growth, which slowed down their recovery process. But looking at current scenarios, we can see that there are various signs of progress amidst the tribulations.
This blog post will provide insight into Sri Lanka’s recent comeback from the economic crisis with a complete analysis till 2023, along with potential opportunities for development strategies for boosting its economy going forward.
So get ready to understand how this small island country is putting all odds against them towards achieving sustainable growth and stability!
Content Highlights
- Sri Lanka has taken several measures, including curbing subsidies and introducing an income relief program, to return from its economic crisis.
- India provided aid worth $2.5 billion and technical assistance to support the country’s recovery efforts.
- Sri Lanka’s failed IMF review has generated an element of uncertainty in terms of when more money will be available for the country to implement key reforms and investments needed for growth.
- Going forward, policies should focus on creating attractive investment opportunities through technology adoption and fiscal discipline with timely repayments towards debt obligations so that the path out of the crisis is smoother into a brighter economic future.
Overview of Sri Lanka’s Economic Crisis (2019-2022)
Sri Lanka has faced a serious economic crisis after the COVID-19 pandemic, and they were in deep trouble during 2022.
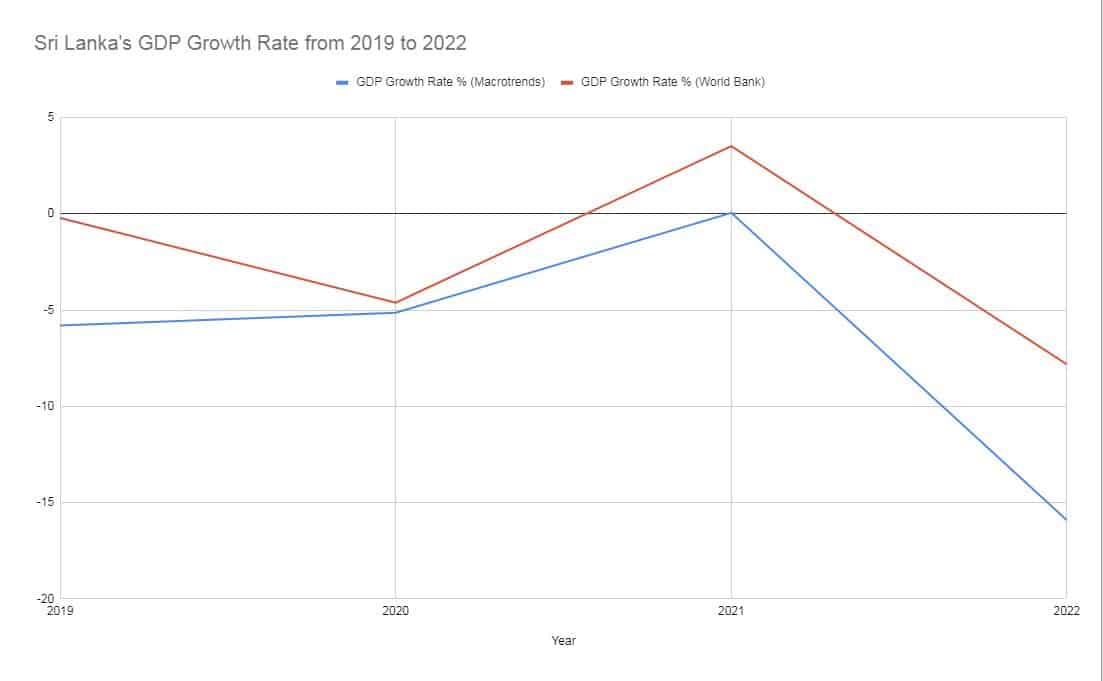
GDP Growth Rate from 2019 to 2023
The data presented below from the two sources shows a consistent directional trajectory, even if the exact growth rates differ somewhat between Macrotrends and the World Bank. Both confirm Sri Lanka’s GDP contracted sharply in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
|
Year |
GDP Growth Rate % (Macrotrends) |
GDP Growth Rate % (World Bank) |
|
2022 |
-15.92 |
-7.82 |
|
2021 |
0.048 |
3.51 |
|
2020 |
-5.14 |
-4.62 |
|
2019 |
-5.80 |
-0.22 |
Table: Yearly GDP Growth Rate of Sri Lanka
According to the World Bank, Sri Lanka recovered in 2021, with GDP growth rebounding to 3.51%. However, the recovery was short-lived, as both sources show the economy contracted again in 2022 as Sri Lanka grappled with a severe economic crisis.
The -15.92% GDP decline in 2022 per Macrotrends is remarkably severe and highlights just how dramatically the crisis impacted the Sri Lankan economy last year. This double-digit plunge far exceeds the contractions seen even during COVID in 2020.
Driving the economic calamity in 2022 were currency devaluations, supply chain disruptions, inflation, debt defaults, and political instability. The crisis crippled Sri Lanka, leading to shortages of essentials like food, fuel and medicines.
Going forward, Sri Lanka faces major challenges in restoring macroeconomic stability and investor confidence. Debt restructuring negotiations with the IMF and creditors will be key. But the road to recovery looks long for an economy that saw its worst contraction in decades in 2022.
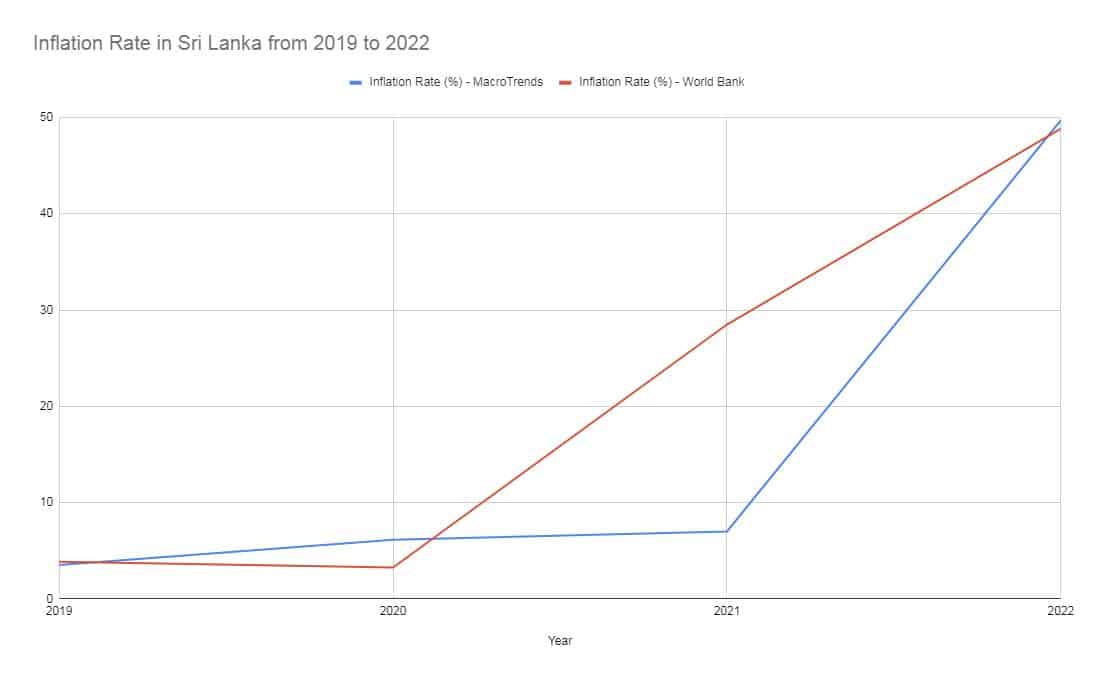
Inflation Rate from 2019 to 2023
New data reveals just how dramatically inflation escalated in Sri Lanka during the recent economic crisis. According to statistics from MacroTrends and the World Bank, the island nation went from low single-digit inflation in 2019-2020 to crisis-level spikes in 2022.
|
Year |
Inflation Rate (%) – MacroTrends |
Inflation Rate (%) – World Bank |
|
2022 |
49.72 |
48.84728 |
|
2021 |
7.01 |
28.496119 |
|
2020 |
6.15 |
3.2709028 |
|
2019 |
3.53 |
3.8705283 |
Table: Yearly Inflation Rate of Sri Lanka
The World Bank registered inflation crossing into double-digits in 2021 before skyrocketing to nearly 49% by 2022. MacroTrends data similarly shows inflation accelerating from 3.53% in 2019 to over 49% last year.
The runaway price increases have been attributed to shortages, supply chain woes, local currency devaluation, and surging global commodity prices. For ordinary Sri Lankans, it has meant severe erosion of real incomes.
Bringing inflation back under control will be critical for restoring stability. Tighter monetary policy and fiscal discipline will be key to lowering inflation over the medium term, economists say.
Causes of the crisis
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating impact on Sri Lanka’s tourism industry, with the huge decrease in foreign tourists leading to financial implications for the country. In addition to this, mismanagement of funds and inappropriate fiscal and monetary policies have long been credited as the main factors behind Sri Lanka’s economic crisis.
Tax cuts implemented by some previous governments have contributed, too, making it harder for the government to fund essential projects or services related to healthcare and infrastructure.
This has caused severe shortages of essential goods such as food, medicines, and cooking gas, in turn deepening the economic crisis. It is important to note that China is not responsible for Sri Lanka’s current economic woes.
Impact on the country
As a result of the economic crisis in Sri Lanka, many negative effects have been felt throughout the country. Tourism, one of the main drivers of the Sri Lankan economy, witnessed a sharp decline as travelers chose to stay away for fear of contracting COVID-19.
Similarly, remittances also took a huge hit as many repatriated expatriates opted to remain in their home countries due to lockdowns and travel restrictions. The whole atmosphere in Sri Lanka suffered from pessimism and uncertainty over potential job losses and falling incomes.
As businesses were forced to close down or reduce staff numbers due to a lack of customer demands or cash flow issues, families had difficulty making ends meet, leading to an increase in poverty levels across certain sections of society. However, Sri Lanka is now gradually opening for business, as per the latest news.
Measures taken to address the Economic crisis
[Video Credits @DW News]
The Government of Sri Lanka, under the leadership of President Ranil Wickremasinghe, implemented a series of policy reforms and measures to address the economic crisis in 2019. These include:
Monetary Policy Measures
To tackle high inflation that peaked at nearly 70% in 2022, Sri Lanka’s central bank cut policy rates by 450 basis points between June and July 2023. This monetary easing was enabled by the decline in inflation to just 1.3% by September 2023. The loosening has helped reduce short-term interest rates as well.
Fiscal Policy Measures
On the fiscal side, the government has introduced new taxes and adjusted tax rates/bases to mobilize revenue critical for macroeconomic stability. While this has improved fiscal progressivity, rising indirect taxes and energy costs disproportionately impact the poor. Targeted relief measures are needed to offset this impact.
External Sector Measures
Import restrictions and weak demand helped shrink the trade deficit despite falling exports. Remittances and tourism earnings also improved, boosting foreign reserves. Sri Lanka even offers free tourist visas to 7 countries to boost their tourism economy, targeting to hit 5 million tourist arrivals annually by 2026..
With large debt payments absent, foreign exchange pressures have eased, allowing currency appreciation after sharp depreciation in 2022.
Structural Reforms
Critical reforms, like those related to debt restructuring, remain works in progress. Continued reform implementation across sectors will be key for sustainable growth. The government should couple revenue mobilization efforts with transparency in public expenditure to build confidence.
In summary, Sri Lanka has employed a mix of monetary, fiscal, external sector, and structural policy measures to stabilize the economy after its 2022 crisis. Sustaining reform momentum remains vital for lasting recovery.
Sri Lanka’s Stabilization Efforts
The Wickremasinghe government has implemented key austerity measures, received aid from India, and made substantial progress toward stabilizing the economy.
Role of the Wickremasinghe government
The Wickremasinghe government played a crucial role in Sri Lanka’s recent comeback from the economic crisis. The government implemented measures to boost confidence, stabilize the economy, and reduce poverty levels in the country.
Among the initiatives taken was the restructuring of local debt, through which President Ranil Wickremesinghe reassured citizens that these changes would harm no one member of the Employees’ Provident Fund.
In addition, greater emphasis was placed on promoting self-sufficiency among citizens to create jobs and generate income and expanding welfare support, particularly for those hardest hit by the crisis, e.g., youth unemployment schemes or subsidization of housing loan interest rates so more families could access them easily.
Aid from India
India has been supporting Sri Lanka’s recovery from its economic crisis since 2019. To meet the budget requirements of the country, India provided a financial assistance package worth $2.5 billion – including credit facilities for fuel and food – to help it combat inflation, fiscal deficit wellbeing, and safeguard foreign reserves.
This includes providing funds in local currency equivalents through a swap arrangement and extending lines of credit which can be used to buy necessary fuel and food products during times of need.
The funds are also being used to assist with social protection programs for the vulnerable groups affected by the crisis.
Challenges Faced by Sri Lanka

Sri Lanka faces a number of significant economic and financial challenges restricting its progress, including debt burden, inflation, and low GDP growth. Find out more about the country’s struggles in this article.
Debt burden
Sri Lanka has accumulated a heavy foreign debt of $36 billion, much of it coming from international sovereign bonds worth $12.5 billion. This has been increasingly and rapidly taken on since 2007, leading to a total public debt pile now standing at over $52 billion, as estimated by the World Bank in December 2022.
Although local borrowing counts for just under 55% of this overall public burden – primarily central government debt – its sheer size is cause for alarm and deeply concerning to many Sri Lankan citizens when combined with external creditors.
It raises questions about the stability of their currency, the Sri Lankan rupee, given that a large proportion must be paid back either via principal payments or interest in foreign currencies still vulnerably exposed to forex movements even after payment on loans occurs.
Inflation
Inflation in Sri Lanka has drastically increased since 2019, with the inflation rate rising from a single digit of 5% to 57.2%, far above the global average inflation of 10.1%. This rise in prices is due to various factors such as high-interest rates, falling exports, and import restrictions, leading to stronger demand for imports while at the same time decreasing local supplies, which causes further price increases.
The resulting high cost of living has had an adverse impact on citizens’ purchasing power, and economic growth slowed down significantly since then. With non-food items becoming increasingly expensive, Sri Lankans have had less money available for savings and investments, thus contributing negatively towards GDP growth.
As per IMF figures, during 2021 Q3, economic contraction reached 11.5% largely due to continued high inflation, which continues to act as a further impediment hindering recovery prospects in spite of government efforts targeted at stabilizing currency exchange rates; however, limited success achieved so far.
Low GDP growth
Low GDP growth has been an enduring problem for Sri Lanka’s economy. It peaked in 2019 when the foreign exchange crisis hit, leading to the negative economic growth of 11.5 percent in the first quarter and 3.1 percent in the second quarter.
The country recovered somewhat during 2020, posting 1.6 percent GDP growth by year-end.
However, this was still far away from pre-crisis levels. Despite stabilization efforts implemented by the Wickremasinghe government that were aided by additional financial support from India and other countries, progress has been slow due to the growing debt burden as well as high inflationary pressures caused by low demand for goods and services domestically as well internationally induced recessionary conditions due to impacts of COVID19 pandemic globally.
In order for Sri Lanka to build up sufficient momentum toward sustainable economic recovery, concerted measures should be taken both on fiscal and monetary fronts, with an enhanced focus on improving the investment climate while maintaining macroeconomic stability through appropriate policy measures such as prudent fiscal consolidation efforts complemented with sound monetary policies.
Resilience and Progress Amid the Crisis
Since the onset of Sri Lanka’s economic crisis in 2019, much progress has been made towards stabilization, and the country is now on its way to recovery. Key measures taken by the Wickremasinghe government included making extensive infrastructure investments, reducing subsidies on fuel rather than increasing taxes, and introducing an income-tax relief program that benefited low and middle-income households.
In late 2020, India extended a loan package of $580 million that boosted key sectors such as tourism and health care. This increased confidence in Sri Lanka’s economy both domestically and internationally which helped boost investment levels throughout 2021.
By 2022 inflation had stabilized at 6%, and consumer spending remained strong, with growth in retail sales hitting 7% while exports grew 3%. The GDP began to grow again by 2022, driven largely by increased public expenditure, primarily from Indian aid, followed by further foreign direct investment.
Signs of recovery
While Sri Lanka’s recovery process is ongoing, there are signs of improvements in the economy. Government efforts have led to steady progress against inflation over recent months.
In addition, domestic demand has appreciated as households and businesses were able to sustain consumption levels during the crisis. Summing up, the GDP growth rate increased by 3.2% in the first quarter of 2023 from 2.6% in early 2020 – an indication that the country is slowly recovering from its economic setbacks caused by last year’s events.
Moreover, both foreign direct investments and remittances registered rather positive trends throughout the worst period of this financial downturn which helped sustain private investment into economic activities such as manufacturing base and emerging services like IT/ITES sectors despite challenges posed by import restrictions as well as restrictions on trade imposed in some countries around Sri Lanka including Singapore & India (Covid-19 second wave).
Role of the new government
The Wickremasinghe government has been instrumental in ensuring Sri Lanka’s economic recovery, tackling the challenges posed by the recent crisis. Their leadership was decisive in providing immediate aid to sectors of the economy most affected by it, such as agriculture and more heavily mortgaged households.
Moreover, they pushed for social initiatives aimed at reducing poverty and improving access to healthcare and nutrition. To address structural issues related to debt accumulation, President Ranil proposed reforms ranging from policies that constrained wasteful spending to clearing arrears with foreign contractors, which were responsible for a large share of public debt.
The new government is also focused on spurring growth through 2017-2021’s Economic Transformation Plan, designed as a framework to restore sustainable fiscal management by investing heavily into development projects connected to knowledge-based industries yet adapted specifically towards expanding job opportunities across ages while keeping external debt secured Thanks their policymaking coupled with support from international organizations; Sri Lanka is making headway in its journey back toward economic stability despite confronting major hurdles along the way ahead.
Assistance from international organizations
The economic crisis in Sri Lanka saw the country become dependent on assistance from other countries and international organizations to recover quickly. India, China, Japan, the United States, and other nations provided bailouts during 2017-2020, unlocking much-needed finance that helped arrest a looming financial collapse of the island nation.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) also agreed to be tasked with a four-year Stand-By Arrangement Program providing around $700 million worth of aid packages to support immediate recovery efforts in 2023 as Sri Lanka sought financial support from the IMF back in 2022.
Moreover, major regional players, including the World Bank, provided hundreds of millions for poverty reduction-related projects while more loans were gained from institutions like the Asian Development Bank specifically targeted at improving public services, etc.
At present various programs managed by UNICEF are helping children through school feeding programs and allaying health concerns prevailing in certain zones due to economic hardships experienced since 2019.
Lessons Learned from the Crisis
The crisis has highlighted the importance of economic resilience and prudent management of resources, as well as the need to take proactive measures to address vulnerabilities before they cause irreversible damage.
Addressing economic vulnerabilities
The economic crisis in Sri Lanka, which began in 2019, was the country’s worst economic and political crisis since independence. The cause of the crisis was attributed to a combination of factors, including financial fragility and lack of reform.
In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic had an immense impact on key sectors such as tourism and remittances. For example, data showed that arrivals from mainstay markets such as India and China dropped significantly compared to pre-COVID numbers in 2020, thus negatively impacting revenue for hotels and restaurants located near tourist attractions.
This further exacerbated Sri Lanka’s debt burden leading to a liquidity crunch due to its dependency on capital inflows for external financing. As a result, Sri Lanka needed wide-ranging economic reforms to address vulnerabilities related to macroeconomic imbalances as well as lift longer-term growth prospects while also gaining access them funds from International Monitory Funds (IMF).
Importance of good governance
Good governance is essential in overcoming economic crises and achieving sustainable growth. Having strong leadership with clear objectives and decision-making processes enables a country to anticipate, plan for, and manage the risks associated with crisis, both short-term recovery efforts as well as long-term goals.
This includes ensuring the trustworthiness of financial systems, having effective approaches to taxation, providing access to necessary resources such as healthcare or education assistance, and maintaining transparency when dealing with global investments.
In Sri Lanka’s case, the Wickremasinghe government stabilization plans combined with assistance from India played a key role in slowly emerging out of its recent economic crisis – demonstrating the importance data-driven analysis considering risks and opportunities can have on successful crisis management strategies.
The Road to Sustainable Growth
Utilizing existing opportunities and strategies carefully, Sri Lanka can work towards achieving economic sustainability with the aid of International organizations.
Opportunities for development
In Sri Lanka’s effort to recover from the economic crisis, several opportunities for development are available. The government has introduced structural reforms to shift towards a more efficient and productive economy that will lead to sustainable growth in the long run.
These include greater emphasis on export-led production, industrial diversification, better provision of public goods and services, and improved access to investment capital.
Technology plays an important role in this transformation, with the country leading digitalization efforts in South Asia. Digital platforms such as e-commerce and fintech have sparked new job creation, which can help contribute towards increased levels of employment which was adversely affected by the crisis.
Strategies for economic revival
Here are some potential strategies Sri Lanka could pursue to revive its economy after the recent crisis:
- Pursue debt restructuring with the IMF, China, and other creditors to ease heavy debt repayment burdens. This will free up fiscal resources for growth.
- Implement structural reforms such as improving public finance management, strengthening social safety nets, increasing trade competitiveness, and promoting private sector growth. This will boost productivity.
- Liberalize trade policies by reducing tariffs and para-tariffs. This will make imports cheaper and improve export competitiveness.
- Privatize or restructure state-owned enterprises to improve efficiency and financial performance. This will ease fiscal pressures.
- Maintain prudent monetary policy to curb inflation and ensure exchange rate stability. This will improve macroeconomic conditions.
- Increase foreign currency reserves through bilateral and multilateral assistance, better remittance policies, and higher foreign investment. This will stabilize the currency.
- Expand social welfare programs to protect the poor and vulnerable from economic hardships. This will reduce inequality and raise living standards.
- Improve ease of doing business by cutting red tape, improving access to finance for SMEs, and strengthening legal institutions. This will encourage investment.
- Invest in human capital and skills training to create a productive workforce suited for high-value industries. This will boost competitiveness.
- Promote tourism by improving services, infrastructure, and marketing. This can increase foreign exchange earnings over time.
- Pursue trade agreements to get preferential access to key export markets. This can boost export growth over the long run.
- Follow the fastest economically growing countries to adopt their strategies to overcome the situation as fast as possible.
Role of Technology in Sri Lanka’s Economic Recovery
[Video Credits @Wion]
With technological advancements, the country can leverage its large digital base to harness economic opportunities and create a sustainable future for Sri Lanka.
Impact of digitalization
The use of digital technologies has become increasingly prominent in Sri Lanka’s strategy for recovery from the economic crisis. Digitalization is accelerating in various sectors, focusing on driving automation, increasing contactless payments, and developing virtual experiences.
The country’s digital economy strategy promotes tech-enabled solutions to help address the issues faced during times of crisis, such as shortages of food supplies and insufficient health services.
In addition, the role of technology is seen as critical to strengthening access to financial inclusion; almost 82 percent of citizens are now connected digitally through mobile phones or other devices.
Moreover, it also boosts resilience against future shocks due to its ability to quickly recalibrate business models at lower costs than their traditional counterparts. For example, rapid advances have been made in the tourism industry, where hotels utilize online platforms and consumer data analytics for personalized customer service experiences while several banks focus on launching innovative products such as mobile wallets and merchant wallets that ensure secure transaction processing services for customers nationwide.
As more people adopt modern banking practices with technological support systems like biometric authentication capabilities or facial recognition software becoming common features among banks around the world, which further facilitates smooth transactions with faster response time, gives an additional boost to traditional banking infrastructure by embracing new payment methods enabling them offer much better IT infrastructures significantly improving.
E-commerce potential
With the growing use of digital technology worldwide, e-commerce has become an integral part of economic recovery and growth in developing countries such as Sri Lanka. This is especially true in the aftermath of crisis situations where traditional commerce may not be able to sustain local businesses.
The adoption of e-commerce solutions has grown drastically among small and medium enterprises (SMEs) across multiple sectors, including apparel manufacturing, retail outlets, logistics, and even banking services.
Integrated online platforms have enabled companies to remain competitive by providing access to global markets with lower overhead costs and increased scalability. Moreover, SMEs benefit from automated solutions, which help reduce manual labor while decreasing operational costs.
The crash of the local footwear business in Sri Lanka is a case study that emphasizes the need for alternative avenues, such as an e-commerce platform for sustainable growth during times of economic downturns or geopolitical uncertainties.
As a result, e-commerce provides an opportunity for businesses to diversify their product offerings both nationally as well internationally. With greater technological advances being made around us every day, leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence can also increase efficiency significantly, allowing entrepreneurs turnaround time at scale.
Takeaway
The recent economic crisis in Sri Lanka has been a difficult experience for the country. However, it also allowed policymakers to address vulnerabilities and lay the groundwork for sustainable growth going forward.
The Wickremasinghe government’s stabilization efforts successfully reduced the impact of the crisis on everyday life, while external assistance from India enabled them to stem further downturns and keep GDP positive.
Encouragingly, signs of recovery are now emerging – a 3.6% increase in GDP during Q1 of 2023 indicates progress towards sustainable growth over time. In order to prompt this sustained revival, though, Sri Lanka must reassess its fiscal position and ensure wise public expenditure; administrative reforms must occur to avoid further debt accumulation – particularly as without IMF support, rates surely hedge upwards if timely repayments aren’t made soon enough.
Going forward, governments should look at strategies promoting development, such as creating an attractive business environment, encouraging new investments, and investing in technology.
Technological adoption can help spur innovation & digitalization, reviving multiple industries amid a decline in export-driven sectors like tea & tourism due to current pandemic restrictions- paving a path or ‘blueprint’ out of the crisis for other similarly positioned countries going through similar experiences.