Are you planning to build an eco-friendly home but can’t decide between a passive house and a net-zero home? Many homeowners feel stuck when choosing between these two green building options.
Both types promise big energy savings, but they work in different ways. You want to make the right choice for your budget and the planet.
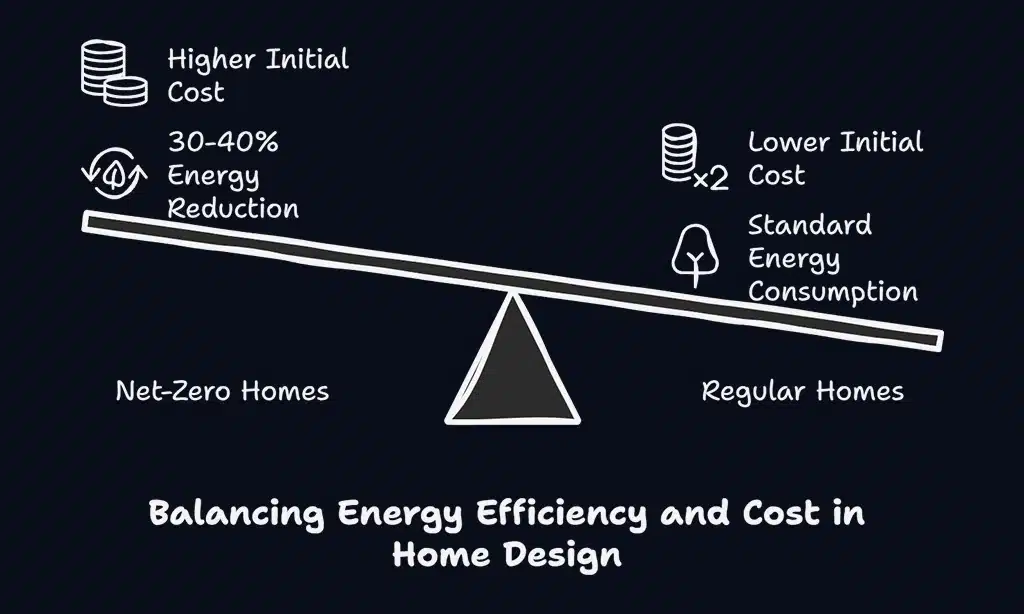
A passive house focuses on cutting energy use through smart design and better insulation. Net-zero homes aim to make all the energy they need using solar panels and other clean sources.
Most people don’t know that a passive house can slash heating costs by up to 90% compared to regular homes.
This guide breaks down the seven main differences between passive houses and net-zero homes. We’ll look at their costs, design features, and how they save energy. You’ll learn which option fits your goals and budget best.
Ready to find your perfect green home?
What Is a Passive House?
A Passive House stands as a super-tight building that cuts energy use by up to 90%. These homes focus on keeping warm air in during winter and hot air out in summer. The design relies on thick insulation, special windows, and careful sealing of all gaps.
Think of it like a thermos that keeps your coffee hot without needing more heat.
The secret lies in strict building rules that make these homes work so well. Builders must use top-grade materials and smart building methods to meet these rules. The walls pack extra insulation, while high-performance windows stop heat from escaping.
The house stays cozy through smart design rather than big heating bills. The air stays fresh through special vents that save most of the heat that would normally go out with stale air.
What Is a Net-Zero Home?
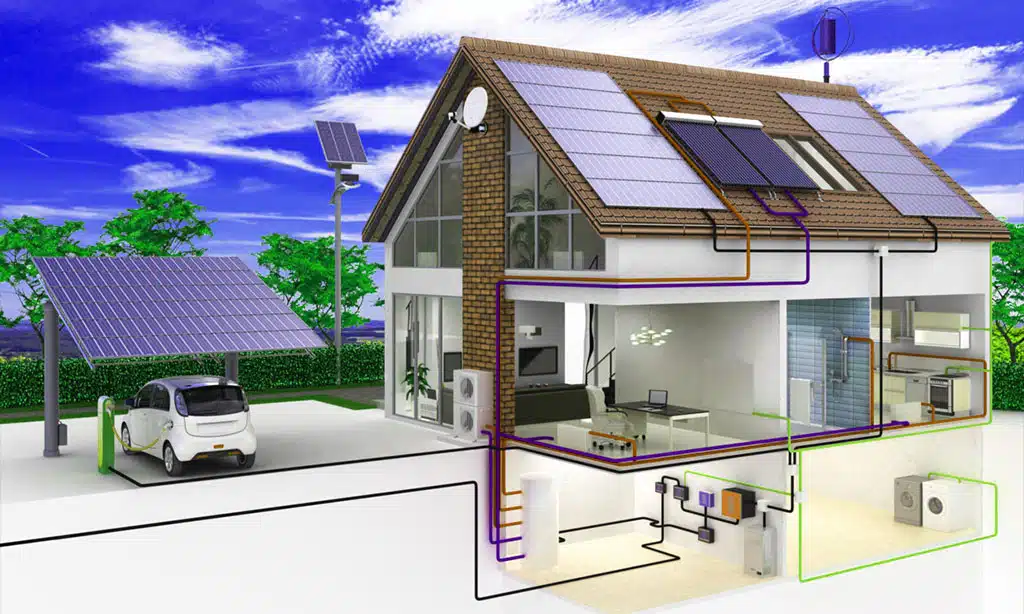
Net-zero homes stand as modern marvels in green building. These homes create as much energy as they use over a year through solar panels, wind power, or other clean energy sources.
The magic happens through smart design and renewable energy systems working together. Most net-zero homes cut their heating and cooling needs by 30-40% compared to regular houses. They mix energy-saving features with power-making tools like solar arrays and battery storage.
Net-zero isn’t just about saving energy – it’s about making your own power right where you live.
These special homes cost about twice as much as regular houses to build. The higher price comes from adding solar panels and other renewable systems. Net-zero homes follow less strict rules than passive houses, which means builders have more freedom in design choices.
The focus stays on matching energy use with clean power made on site. Solar panels often cover the roof, while better insulation and windows help keep indoor temps just right. Some homes also use geothermal energy or wind turbines to reach their zero-energy goals.
Key Principles of Passive House Design
Passive house design focuses on five main rules to cut energy use. Super-thick insulation wraps the whole house like a warm blanket. High-performance windows and doors keep heat inside during winter and outside in summer.
The house needs to be airtight, with special seals around every opening. A ventilation system with heat recovery brings in fresh air while saving energy. These features help passive houses use 30-40% less energy than regular homes.
The building process follows strict rules to make passive houses work well. Builders must pay close attention to thermal bridging, which stops heat from leaking through walls and floors.
They also need careful air sealing to meet the tough standard of 0.6 air changes per hour. Special building materials cost more upfront but save money over time. Good insulation and air-sealing make passive houses very quiet and comfy to live in.
Key Principles of Net-Zero Home Design
Net-zero homes focus on making energy and using less power. These homes need solar panels, good insulation, and smart heating systems to work well. They cut energy use by 30-40% compared to regular homes.
The main goal is to create as much power as they use each year through clean energy sources like solar and wind.
A net-zero house costs about twice as much as a normal home. The design puts solar panels on the roof and uses high-quality windows to keep heat in. The house needs good air flow systems and water heaters that save energy.
Most net-zero homes use heat pumps and special tools to track how much power they make and use. The building plans must think about where the sun shines and how to keep rooms warm or cool.
7 Key Differences Between Passive House and Net-Zero Homes
Passive houses and net-zero homes show clear differences in their design and cost. These two green building styles take different paths to save energy, from how they handle heat to the way they use solar power.
Energy Efficiency Standards
Net-zero homes and passive houses follow different rules for saving energy. A passive house must meet strict building rules that focus on air-tight walls, super insulation, and special windows.
These homes cut heating and cooling needs by 30-40% more than regular houses. The building rules make sure the house stays warm in winter and cool in summer without using much power.
Net-zero homes have more flexible standards but need to make all their own power. They use solar panels, wind power, or other clean energy to match what they use each year. Both types of homes help the earth, but passive houses focus more on using less energy through smart building choices.
Net-zero homes can use more energy if they make enough clean power to balance it out.
Renewable Energy Integration
Passive houses and net-zero homes treat renewable energy very differently. Passive houses focus on cutting energy needs through smart design and building methods. They use thick walls, special windows, and tight seals to slash energy use by up to 90%.
Solar panels or wind power are nice extras but not required in passive houses.
Net-zero homes make renewable energy their main focus. These homes need solar panels, wind turbines, or other clean power sources to make all the energy they use each year. Most net-zero homes install large solar arrays on their roofs or nearby land.
The panels must create enough power to run everything from lights to heating systems. This setup costs more upfront than a regular house, often double the price. But the energy savings help owners get that money back over time through lower utility bills.
Heating and Cooling Systems
Passive houses and net-zero homes handle heating and cooling in different ways. Net-zero homes often use standard HVAC systems with solar panels or other clean energy to power them.
These homes cut heating and cooling energy use by 30-40% compared to regular houses. They might add air source heat pumps or geothermal systems to boost savings.
The focus in passive house design stays on natural ways to keep temps steady. These homes need less power for heating and cooling thanks to thick walls, great insulation, and special windows that stop heat loss.
Most passive houses use heat recovery ventilators to keep fresh air moving while saving energy. The mix of smart design and top-notch materials helps create cozy spaces without big power bills.
Construction Costs
Building a passive house costs more upfront than a standard home. The extra money goes into special materials and building methods. You’ll spend more on thick walls, top-quality windows, and better sealing.
These homes need about twice the budget of regular houses to build.
Net-zero homes have different cost factors. Most of the extra money goes into solar panels and other power systems. The basic building costs stay closer to normal home prices. The total cost rises by 30-40% above standard homes.
Solar panels and energy storage make up the biggest part of this increase. Many homeowners get this money back through lower energy bills over time.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Passive houses need less money to run each year. Their super-tight walls and great windows keep heat inside better than regular homes. This means lower bills for heating and cooling all year long.
The special air systems in passive houses also clean indoor air better, which cuts down on health costs.
Net-zero homes cost more to keep up because they use lots of gear like solar panels and wind turbines. These parts need regular checks and fixes to work right. Still, the money you save on power bills helps balance these costs.
Most net-zero homes save 30-40% on heating and cooling compared to normal houses. The solar panels and other parts might need to be fixed or changed every few years to keep making power.
Design Flexibility
Net-zero homes offer more design choices than passive houses. You can build a net-zero home in many styles because it focuses on making energy, not just saving it. The rules for passive houses limit some design options.
They need specific window sizes, building shapes, and wall thickness to meet strict energy rules.
Building a passive house means following exact rules about how to build it. Net-zero homes give you more room to play with the design. You can pick from different ways to make energy, like solar panels or wind power.
The main goal is to create as much power as you use in a year. This freedom lets builders mix modern and classic styles while still hitting energy goals.
Environmental Impact
Passive houses and net-zero homes both help our planet, but they do it in different ways. Passive houses cut down on energy use from the start through smart building choices like thick walls and special windows.
These homes need less power to stay warm or cool, which means they put out fewer harmful gases into the air. The focus stays on using less energy rather than making more of it.
Net-zero homes mix energy saving with green power creation. They might use solar panels or wind power to make up for the energy they use. These homes can still help fight climate change, even if they use more energy than passive houses.
The key lies in making enough clean energy to cancel out what the house needs. Both types of homes shrink their carbon footprint, but passive houses do it by needing less power in the first place.
Takeaways
Both home designs offer great ways to save energy and help the planet. Net-zero homes focus on making their own power through solar panels and wind energy. A passive house cuts energy use through smart building tricks like thick walls and special windows.
Your choice depends on your budget and what matters most to you. Smart homeowners can mix ideas from both styles to create an eco-friendly home that works best for their needs.
FAQs
1. What makes a passive house different from a net-zero home?
A passive house focuses on reducing energy consumption through super insulation and heat recovery ventilation. Net-zero homes use renewable energy sources like solar panels to make as much energy as they use.
2. Which costs more to build, a passive house or a net-zero home?
Passive houses often cost more upfront due to special insulating materials and high-performance windows. Net-zero homes can be less expensive to build but need solar panels or wind turbines added.
3. Do passive houses need solar panels?
No. Passive houses rely on passive solar design and thermal mass to stay warm, not solar panels.
4. Can net-zero homes work off the power grid?
Yes, net-zero homes can work off grid when they combine solar energy, energy storage, and backup systems to meet all power needs.
5. Which home type is better for reducing carbon emissions?
Both help cut carbon footprints. Passive houses use very little energy for heating and cooling. Net-zero homes make clean energy to offset what they use.
6. What are the main heating methods in these homes?
Passive houses use heat recovery ventilation and passive solar heating. Net-zero homes often combine geothermal energy, radiant heating, and solar water heaters to stay warm.