In recent years, the global energy landscape has undergone a significant transformation, with renewable energy sources becoming increasingly cost-competitive compared to traditional fossil fuels.
This shift has led many to ask: Is green energy cheaper than fossil fuels? The answer is a resounding yes, as evidenced by recent data and industry trends.
The Changing Landscape of Energy Costs
In recent years, the cost of renewable energy technologies has plummeted, making them more competitive with fossil fuels. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global weighted average cost of electricity from newly commissioned utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) projects fell by 13% between 2020 and 2021, reaching $0.048 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Similarly, onshore wind costs decreased by 15% to $0.033/kWh.
These price reductions have made renewable energy sources not only competitive but often cheaper than fossil fuel alternatives. In fact, IRENA reports that in 2021, 81% of newly added renewable power capacity had lower costs than the cheapest new fossil fuel option.
Comparing Costs: Renewables vs Fossil Fuels
To better understand the cost comparison between green energy and fossil fuels, let’s look at some specific data:
| Energy Source | Cost per MWh (2023) |
| Solar PV | $31-$42 |
| Onshore Wind | $26-$50 |
| Coal | $65-$159 |
| Natural Gas | $45-$74 |
Source: Lazard’s Levelized Cost of Energy Analysis (2023)
As the table shows, both solar PV and onshore wind have become significantly cheaper than coal and are often less expensive than natural gas. This trend is expected to continue as renewable technologies improve and economies of scale are realized.
Factors Driving the Cost Reduction of Renewable Energy
Several factors have contributed to the declining costs of renewable energy:
- Technological advancements
- Economies of scale in production
- Improved efficiency in manufacturing processes
- Increased competition among suppliers
- Supportive government policies and incentives
These factors have combined to create a virtuous cycle of cost reduction, making renewable energy increasingly attractive to investors, utilities, and consumers alike.
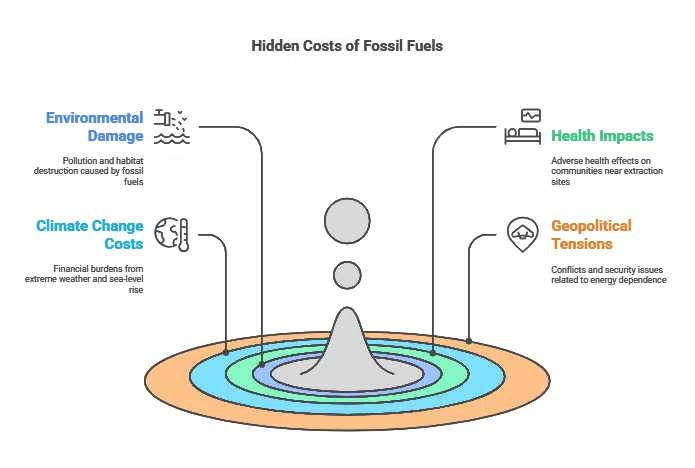
The Hidden Costs of Fossil Fuels
While the direct costs of fossil fuels may sometimes appear competitive, it’s crucial to consider the hidden or externalized costs associated with their use. These include:
- Environmental damage and pollution
- Health impacts on communities near extraction sites and power plants
- Climate change-related costs (e.g., extreme weather events, sea-level rise)
- Geopolitical tensions and energy security concerns
When these factors are taken into account, the true cost of fossil fuels becomes significantly higher than that of renewable energy sources.
Economic Benefits of Transitioning to Green Energy
The shift towards renewable energy is not just about cost savings; it also presents significant economic opportunities. A study by Oxford University researchers found that transitioning to clean energy could save the world as much as $12 trillion by 2050. This potential saving is attributed to the rapidly falling costs of renewable technologies and the avoided costs associated with fossil fuel use.
Moreover, the renewable energy sector is becoming a major source of employment. The International Labour Organization estimates that the transition to a greener economy could create 24 million new jobs globally by 2030.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising trends in renewable energy costs, there are still challenges to overcome:
Intermittency and Storage
One of the main criticisms of renewable energy sources like solar and wind is their intermittent nature. However, advancements in energy storage technologies, particularly battery storage, are addressing this issue. The cost of battery storage has fallen by 89% between 2010 and 2023, making it increasingly feasible to integrate large amounts of renewable energy into the grid.
Infrastructure and Grid Integration
Transitioning to a renewable-based energy system requires significant investments in infrastructure and grid modernization. While these upfront costs can be substantial, they are often offset by the long-term savings and benefits of renewable energy.
Policy and Regulatory Environment
Supportive policies and regulations play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of renewable energy. Governments worldwide are implementing various measures, such as carbon pricing, renewable portfolio standards, and tax incentives, to encourage the transition to clean energy.
The Future of Energy: Projections and Implications
As renewable energy technologies continue to improve and costs decline further, their dominance in the global energy mix is expected to grow. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that renewable energy will account for 95% of the increase in global power capacity through 2026.
This shift has profound implications for:
- Climate change mitigation: Increased use of renewables will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy security: Countries can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels.
- Economic development: Investment in renewable energy can drive innovation and create new industries.
- Air quality and public health: Reduced fossil fuel use will lead to cleaner air and improved health outcomes.
The Economic Case for Green Energy
The evidence is clear: green energy is not only becoming cheaper than fossil fuels but is also offering numerous additional benefits. From cost savings and job creation to environmental protection and improved public health, the transition to renewable energy presents a compelling economic case.
As we look to the future, it’s evident that the question is no longer whether renewable energy can compete with fossil fuels on cost but rather how quickly we can transition to a clean energy economy. The economic advantages of green energy, combined with its environmental benefits, make it an increasingly attractive option for countries, businesses, and individuals alike.
The transition to renewable energy is not just an environmental imperative; it’s becoming an economic necessity. As costs continue to fall and technologies improve, we can expect to see an acceleration in the adoption of green energy sources worldwide, paving the way for a more sustainable and prosperous future.
Takeaways
The answer is increasingly clear: Is green energy cheaper than fossil fuels? In many cases, yes, especially when considering the hidden costs of fossil fuels. As technology advances and adoption rates increase, the financial and environmental benefits of green energy will only continue to grow.
By investing in renewable energy today, we are not only saving money but also securing a sustainable future for generations to come.