In an era of climate change and environmental awareness, adopting eco-friendly design choices for a sustainable home is more important than ever. Sustainable homes not only reduce carbon footprints but also lower energy costs, improve indoor air quality, and create a healthier living space for occupants.
Whether you’re constructing a new home or upgrading an existing one, making informed decisions about materials, energy sources, and water conservation can have a lasting positive impact on the environment.
By implementing energy-efficient solutions, utilizing renewable resources, and integrating smart technology, homeowners can create eco-conscious spaces that align with modern living standards.
This guide explores 10 eco-friendly design choices for a sustainable home, providing actionable insights, cost comparisons, and case studies to help you build a greener future.
10 Eco-Friendly Design Choices for a Sustainable Home
Designing an eco-friendly home is all about making smart choices that reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and promote sustainability. From insulation to renewable energy sources, every decision plays a role in creating a greener living space.
By incorporating sustainable materials and energy-efficient solutions, you can lower your carbon footprint while enjoying long-term cost savings.
Whether you’re building from scratch or upgrading an existing home, these choices can make a significant difference. Explore these 10 eco-friendly design options to create a healthier and more sustainable home
1. Energy-Efficient Insulation for Reduced Heat Loss
Insulation plays a critical role in minimizing energy loss, reducing heating and cooling costs, and maintaining indoor comfort. Poor insulation can lead to excessive energy consumption, increasing both utility bills and environmental impact.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, properly insulating a home can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 20%.
Best Eco-Friendly Insulation Materials
| Insulation Material | Benefits | Cost Comparison (Per Sq. Ft.) |
| Recycled Denim | Sustainable, non-toxic, excellent thermal performance | $1.10 – $1.50 |
| Sheep’s Wool | Natural, fire-resistant, moisture-wicking | $1.50 – $2.50 |
| Cork | Renewable, biodegradable, mold-resistant | $2.00 – $3.00 |
| Cellulose | Made from recycled paper, low carbon footprint | $0.90 – $1.40 |
Case Study: Iceland’s Eco Homes
In Iceland, homes are designed with sheep’s wool insulation, capitalizing on its natural warmth-retaining properties. Studies show that these homes use 30% less energy than traditional fiberglass-insulated homes.
Pro Tip:
Ensure proper sealing of windows, doors, and attics to maximize insulation efficiency and prevent air leaks.
2. Solar Power: A Renewable Energy Game Changer
Solar energy harnesses the sun’s power to generate electricity, significantly cutting down reliance on fossil fuels and reducing utility costs. With government incentives and declining solar panel costs, homeowners can expect an average return on investment within 5-7 years.
Types of Solar Panels for Homes
| Solar Panel Type | Efficiency | Lifespan | Cost per Watt |
| Monocrystalline | 20-22% | 25-30 years | $1.00 – $1.50 |
| Polycrystalline | 15-17% | 20-25 years | $0.90 – $1.20 |
| Thin-Film | 10-12% | 15-20 years | $0.70 – $1.00 |
Tips for Maximizing Solar Efficiency:
- Install panels facing the sun’s optimal direction.
- Keep solar panels clean for maximum performance.
- Pair solar with a battery backup system for continuous power.
Case Study: Tesla’s Solar Roof
A homeowner in California installed a Tesla Solar Roof and reduced their electricity bill by 85%, saving over $1,200 annually while increasing property value.
3. Sustainable Flooring: Choosing Non-Toxic and Durable Materials
Flooring is a fundamental aspect of home design, and selecting eco-friendly options can significantly reduce environmental impact while improving indoor air quality. Many conventional flooring materials contain harmful chemicals and require extensive resource extraction. Sustainable flooring alternatives offer durability, aesthetic appeal, and lower carbon footprints.
Top Eco-Friendly Flooring Options
| Flooring Type | Pros | Cons | Cost Per Sq. Ft. |
| Bamboo | Durable, renewable | Susceptible to scratches | $3.00 – $8.00 |
| Reclaimed Wood | Unique, reduces waste | Requires refinishing | $5.00 – $15.00 |
| Cork | Soft, soundproof | Can fade in sunlight | $4.00 – $9.00 |
| Recycled Tiles | Long-lasting, stylish | Higher installation cost | $2.00 – $10.00 |
Practical Tips:
- Opt for low-VOC adhesives to avoid indoor air pollution.
- Choose pre-finished flooring to reduce on-site chemical exposure.
Case Study: Eco-Homes in Sweden
Sweden’s green homes feature cork and bamboo flooring, which are both carbon-negative materials, absorbing more CO2 than they emit during production.
4. Smart Water Conservation Systems
Freshwater is a limited resource, and sustainable home design must include water conservation strategies. By using smart water-saving technologies, homeowners can significantly reduce water waste and lower utility bills.
Top Water-Saving Solutions
| Water Conservation Method | Benefits | Cost Range |
| Low-Flow Faucets & Showerheads | Reduces water use by 50% | $10 – $50 per fixture |
| Dual-Flush Toilets | Saves up to 67% more water than standard toilets | $100 – $300 |
| Rainwater Harvesting Systems | Provides water for irrigation and household use | $500 – $5,000 |
| Greywater Recycling Systems | Reuses wastewater for non-potable uses | $1,000 – $5,000 |
Case Study: Australia’s Water-Efficient Homes
Australia’s drought-prone regions have widely adopted rainwater harvesting and greywater systems, reducing household water consumption by up to 40%.
Pro Tip:
Install smart irrigation systems that adjust watering schedules based on weather conditions to maximize efficiency.
5. Passive House Design for Natural Efficiency
Passive house design optimizes natural heating, cooling, and ventilation to minimize energy use. This concept relies on airtight construction, high-performance windows, and strategic building orientation.
Key Elements of Passive Design
| Feature | Benefits |
| Thermal Mass Materials | Absorbs and releases heat efficiently |
| High-Performance Windows | Triple-glazed windows with low-emissivity coatings help regulate indoor temperatures |
| Strategic House Orientation | Optimizes natural light and airflow to reduce energy needs |
Case Study: Germany’s Passive Homes
Germany’s Passive House Institute has developed homes that use 90% less energy than traditional buildings, setting a global standard for energy efficiency.
Pro Tip:
Use light-colored roofing materials to reflect heat and keep interiors cooler in warm climates.
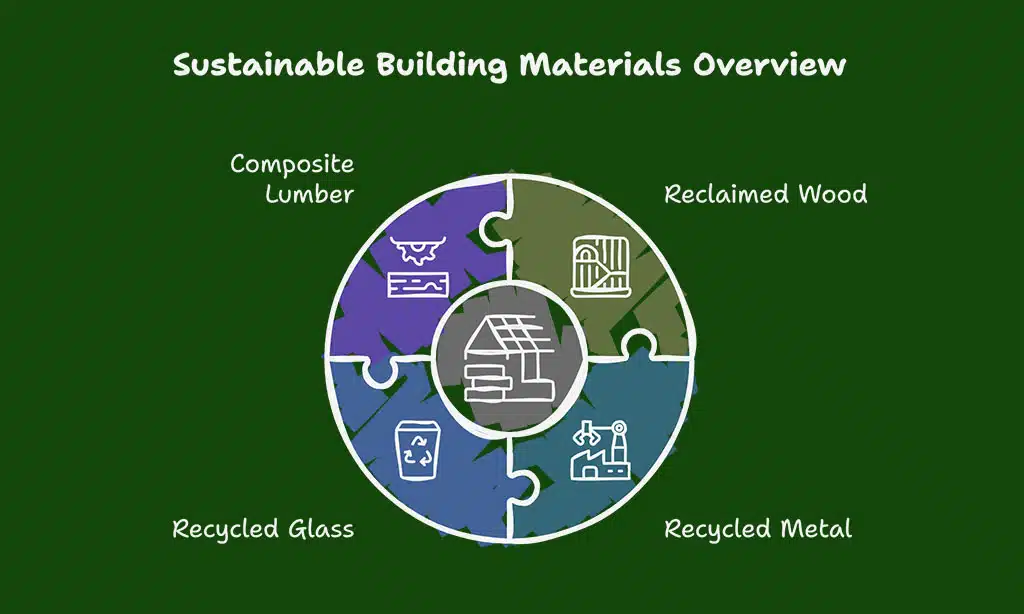
6. Recycled and Upcycled Building Materials
Using recycled and upcycled materials reduces landfill waste and decreases demand for virgin resources. It also adds unique aesthetic appeal to homes.
Best Recycled Building Materials
| Material | Benefits | Common Uses |
| Reclaimed Wood | Reduces deforestation | Flooring, furniture, beams |
| Recycled Metal | Highly durable, energy-efficient | Roofing, fixtures, framing |
| Recycled Glass | Aesthetic appeal, eco-friendly | Countertops, tiles |
| Composite Lumber | Made from recycled plastics and wood | Decking, fencing |
Case Study: The Netherlands’ Circular Homes
Dutch architects have pioneered fully recyclable homes made from modular and sustainable materials, reducing environmental impact.
Pro Tip:
Visit architectural salvage yards to find affordable, high-quality recycled materials for home projects.
7. Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
Inefficient windows and doors contribute to heat loss and gain, increasing energy consumption. Choosing energy-efficient options enhances insulation and reduces utility bills.
Best Sustainable Window and Door Options
| Feature | Benefits |
| Triple-Glazed Windows | Superior insulation and noise reduction |
| Low-E Coatings | Reflect heat, keeping interiors comfortable year-round |
| Fiberglass Doors | Durable, energy-efficient, and recyclable |
| Weather Stripping | Prevents air leaks and enhances insulation |
Case Study: Canada’s Cold Climate Homes
Canadian homes utilize triple-glazed windows to withstand extreme temperatures, reducing heating costs by up to 25%.
Pro Tip:
Consider installing automated blinds or smart window films to optimize energy efficiency.
8. Green Roofs and Living Walls
Green roofs and living walls improve air quality, regulate indoor temperatures, and enhance biodiversity. They also help reduce urban heat islands in cities.
Types of Green Roofing Systems
| Type | Characteristics |
| Extensive Green Roofs | Lightweight, low-maintenance, drought-resistant plants |
| Intensive Green Roofs | Heavier, more diverse plantings requiring structural support |
Case Study: Singapore’s Green Architecture
Singapore has integrated extensive green roof systems in urban buildings, leading to better temperature regulation and energy savings.
Pro Tip:
Select native plants for green roofs and walls to minimize water usage and maintenance needs.
9. Smart Home Technology for Sustainability
Integrating smart home technology optimizes energy consumption, reduces waste, and enhances home security.
Top Smart Home Innovations
| Technology | Benefits |
| Smart Thermostats | Adjusts temperature based on occupancy and weather |
| Energy Monitoring Systems | Tracks and optimizes energy usage |
| Smart Lighting | Automatically dims or turns off lights when not needed |
| Automated Window Shades | Enhances natural lighting efficiency |
Case Study: U.S. Smart Homes
Homes equipped with smart energy systems reduce electricity usage by up to 30%, cutting costs and carbon footprints.
Pro Tip:
Use a home energy audit app to analyze and improve household energy efficiency.
10. Sustainable Landscaping and Outdoor Design
Sustainable landscaping conserves water, supports local ecosystems, and enhances property value.
Best Eco-Friendly Landscaping Practices
| Practice | Benefits |
| Xeriscaping | Uses drought-resistant plants to minimize water needs |
| Permeable Paving | Reduces runoff and enhances groundwater absorption |
| Native Plant Gardens | Supports local wildlife and requires less maintenance |
| Composting Systems | Reduces waste while improving soil quality |
Case Study: California’s Drought-Resistant Landscaping
California homeowners have transitioned to xeriscaping, reducing outdoor water usage by up to 60%.
Pro Tip:
Install a drip irrigation system to deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation.
Takeaways
Designing an eco-friendly home is a meaningful step toward sustainability, reducing environmental impact while creating a healthier living space. By incorporating energy-efficient insulation, solar power, sustainable materials, and smart technology, homeowners can significantly lower their carbon footprint.
With global case studies demonstrating the effectiveness of these strategies, there’s never been a better time to invest in a greener future.
Start small by making one eco-conscious change at a time, and watch as your home transforms into a sustainable haven for years to come.