Listen to the Podcast:
Are you thinking about creatine vs creatinine? Creatine and creatinine are two chemical compounds that share a similar origin and are intricately linked to the functioning of our bodies. And this is now a big confusion among regular people as many of us think they are the same.
But if you think like this you’re wrong. So, are you willing to know the differences between creatine and creatinine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring amino acid synthesized primarily in the liver, while creatinine is a waste product formed during the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells.
Are you now clear they are not the same? I think you’re. So, now to explore things in detail let’s check the detailed guide below.
What Is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring substance found in vertebrates. It is primarily stored in the muscles and brain and is derived from dietary sources such as seafood and red meat. While creatine can be synthesized artificially, it is predominantly produced in the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. Structurally, creatine is a nitrogenous compound with a carboxylic group. It is formed from the amino acids glycine, L-arginine, and L-methionine.
Orally consumed creatine is sometimes used to address various brain disorders, heart diseases, and neurological conditions. In addition, topical creatine is applied to treat signs of skin aging.
It has been explored for its potential benefits in depression, fibromyalgia, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, muscle atrophy and cramps, head trauma, diabetes, schizophrenia, muscle breakdown in the spine, Rett syndrome, gyrate atrophy (an eye disease), Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, breathing problems in sleeping infants, and post-surgical recovery.
What Is Creatinine?
Creatinine is a waste product that is produced when creatine breaks down in muscle cells. The amount of creatine phosphate formed relies on an individual’s muscle mass, and creatinine is eliminated from the body primarily through the kidneys.
It is transported to the kidneys via the bloodstream, where it is filtered and eventually excreted in urine. Men generally have higher levels of creatinine compared to women, primarily due to the presence of greater skeletal muscle mass in men.
Assessing the levels of creatinine in blood and urine helps in calculating creatinine clearance and estimating the glomerular filtration rate, which indicates how well the kidneys are functioning.
If the kidneys are severely damaged or not functioning properly, the rate at which creatinine is cleared from the body will be affected. Low levels of creatinine may indicate conditions such as muscle atrophy, a sedentary lifestyle, malnutrition, debility, or multiple sclerosis.
Creatine vs Creatinine: Quick Overview
Before we elaborately discuss everything let’s get everything in a table for a quick view.
|
Aspect |
Creatine |
Creatinine |
|
Molecular Formula |
C4H9N3O2 |
C4H7N3O |
|
Scientific Name |
2-(carboximidoyl-methyl-amino) acetic acid |
2-amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one |
|
Formation |
Naturally produced in the body and obtained from dietary sources |
A byproduct of creatine metabolism during the breakdown in muscle cells |
|
Excretion |
Not directly excreted, utilized for energy metabolism |
Filtered by kidneys and excreted in urine |
|
Kidney Function |
No specific role, not a marker for kidney function |
Widely used marker to assess kidney function, diagnose kidney diseases |
|
Purpose |
Supplies energy to muscles and nerve cells promotes muscle growth |
Indicator of kidney function, used for kidney health assessment and diagnosis |
|
Side Effects |
Nausea, diarrhea, muscle cramping, stomach pain, irregular heartbeat |
Potential kidney malfunction, swelling, confusion, nausea, shortness of breath |
|
Structure |
A linear molecule with carboxylic acid, amino, and guanidine groups |
Heterocyclic structure with imidazole ring, attached amino and methyl groups |
|
Molar Mass |
131.13 g/mol |
113.12 g/mol |
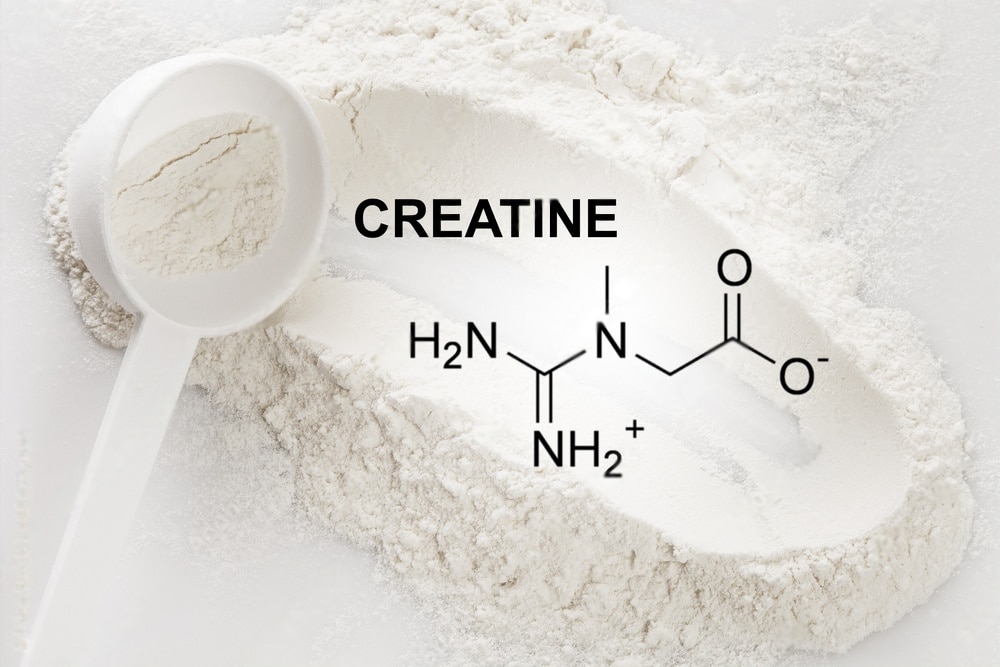
Molecular Formula and Scientific Name
Creatine
- Molecular Formula: C4H9N3O2
- Scientific Name: 2-(carboximidoyl-methyl-amino) acetic acid
Creatine is a nitrogenous organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9N3O2. It is naturally produced in the body and can also be obtained from dietary sources, primarily meat products. Structurally, creatine consists of a carboxylic acid group and an amino group attached to a central carbon atom.
The scientific name, 2-(carboximidoyl-methyl-amino) acetic acid, reflects the chemical structure of creatine. The term “carboximidoyl” indicates the presence of a functional group with a carbon-nitrogen double bond, while “methyl-amino” refers to the attachment of a methyl group to an amino group. The “acetic acid” portion signifies the presence of a carboxylic acid group.
Creatinine
- Molecular Formula: C4H7N3O
- Scientific Name: 2-amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazole-4-one
Creatinine is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C4H7N3O. It is a byproduct of creatine metabolism that is formed during the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells. Creatinine is produced in the body and is also filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine.
The scientific name, 2-amino-1-methyl-5H-imidazol-4-one, describes the chemical structure of creatinine. The term “amino” indicates the presence of an amino group, while “methyl” signifies the attachment of a methyl group to the nitrogen atom. “Imidazole” refers to the ring structure, and “4-one” signifies the presence of a ketone group on the fourth carbon atom of the ring. The “5H” prefix indicates the tautomeric form of the imidazole ring.
Read Also: Creatine vs Pre-Workout: Unveiling the Powerhouses
Significance of Creatine vs Creatinine
Significance of Creatine
Creatine is a highly significant compound in the body due to its various functions and benefits. It is classified as an organic acid and is naturally synthesized within the body. Additionally, it can be obtained from dietary sources, mainly meat products. The significance of creatine includes:
- Energy Generation: Creatine plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, particularly in activities that require short bursts of intense muscular effort. It helps the muscle tissues generate more energy by facilitating the regeneration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for muscle contractions.
- Muscle Growth and Mass: Creatine is closely associated with the growth and development of muscles. It promotes the increase of muscle mass by enhancing protein synthesis and aiding in muscle repair and recovery.
- Neurological Benefits: Studies have suggested that creatine supplementation may have neuroprotective properties. It has shown potential in combating neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, by protecting neurons and improving brain function.
- Diabetes Management: Some research indicates that creatine supplementation may have a positive impact on blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. However, more studies are needed to establish its effectiveness in this area.
- Athletic Performance Enhancement: Creatine is widely used as a dietary supplement by athletes and bodybuilders. Its ability to increase phosphocreatine stores in the muscles leads to improved energy production during high-intensity exercise. This can result in enhanced strength, power, and overall athletic performance.
Significance of Creatinine
Creatinine, while not serving a specific vital function in the body, plays a critical role as an indicator of kidney function. Its significance lies in the following aspects:
- Kidney Function Assessment: Creatinine levels in the blood provide valuable information about the efficiency of kidney function. The kidneys filter creatinine from the bloodstream and eliminate it through urine. Monitoring creatinine levels helps doctors evaluate the overall health and performance of the kidneys.
- Diagnostic Tool: Creatinine tests are commonly used in clinical practice to diagnose certain diseases and conditions related to kidney function. Elevated levels of creatinine in the blood may indicate impaired kidney function and can help identify the presence of kidney diseases or disorders.
- Monitoring Kidney Health: Regular measurement of creatinine levels is essential in monitoring kidney health and identifying any potential issues. Significant increases in creatinine levels may suggest kidney dysfunction, and further testing is typically conducted to determine the extent of the kidney problem and guide appropriate treatment.
Read More: Does Creatine Make You Bloated?
Purpose of Creatine vs Creatinine
Purpose of Creatine
The primary purpose of creatine is to be stored in the muscles, where it exerts its beneficial effects. Its main purposes include:
- Muscle Mass and Strength: Creatine enhances muscle growth and increases muscle mass. By facilitating protein synthesis and supporting muscle repair, it contributes to the development of stronger and more resilient muscles.
- Energy Production: Creatine acts as a crucial component in the process of generating energy for high-intensity activities. It helps replenish ATP levels, allowing muscles to maintain their performance during short bursts of intense exercise.
Purpose of Creatinine
The purpose of creatinine is not to perform a specific function within the body but rather to serve as a marker for kidney function. By measuring creatinine levels, doctors can assess the performance of the kidneys, diagnose kidney-related issues, and monitor the progression of kidney diseases. Elevated
Side Effects
Creatine
When consumed in excessive amounts, creatine supplementation can lead to certain side effects. Here is a more detailed explanation of the potential side effects of high levels of creatine:
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience feelings of nausea or an upset stomach after taking high doses of creatine. This can range from mild discomfort to more pronounced feelings of queasiness.
- Diarrhea: High levels of creatine intake can sometimes lead to an increase in bowel movements and loose stools, resulting in diarrhea. It is important to maintain proper hydration when using creatine to help mitigate this effect.
- Muscle Cramping: In rare cases, individuals taking high doses of creatine may experience muscle cramps. This could be due to dehydration or imbalances in electrolyte levels, such as sodium and potassium. Ensuring adequate hydration and electrolyte balance can help reduce the risk of muscle cramps.
- Stomach Pain: Some individuals may experience stomach pain or discomfort as a side effect of creatine supplementation. This can vary from mild discomfort to more severe pain. It is advisable to take creatine with food or divide the dosage throughout the day to minimize the risk of stomach discomfort.
- Irregular Heartbeat: In some individuals, high levels of creatine consumption may cause irregular heartbeat or palpitations. This side effect is relatively rare and typically occurs in individuals who are predisposed to heart rhythm abnormalities. If such symptoms occur, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
Creatinine
Now have a look at some side effects of creatinine.
- Possible Malfunction or Failure of the Kidneys: Elevated levels of creatinine in the blood can indicate potential issues with kidney function. If the kidneys are not working properly, creatinine levels can rise. This may be a sign of kidney malfunction or failure, and further testing is usually required to assess the extent of the kidney issues.
- Swelling or Edema: High levels of creatinine can sometimes lead to swelling or fluid retention in various parts of the body. This may manifest as swollen legs, ankles, or face. It is important to seek medical attention if significant swelling occurs.
- Confusion: In some cases, increased creatinine levels may be associated with cognitive symptoms such as confusion or difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can indicate underlying kidney problems and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Elevated creatinine levels can contribute to feelings of nausea and may result in vomiting in some individuals. This can be a sign of kidney dysfunction and should be addressed by a medical professional.
- Shortness of Breath and Fatigue: In advanced stages of kidney dysfunction, high creatinine levels can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue. These symptoms may be accompanied by other signs of kidney failure and require immediate medical attention.
- Dehydration: Kidney dysfunction associated with elevated creatinine levels can impair the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance, potentially leading to dehydration. It is important to stay hydrated and seek medical attention if signs of dehydration are present.
Creatine vs Creatinine: Structure
Creatine
The structure of creatine consists of a linear molecule. It is composed of three main functional groups: a carboxyl group (-COOH), an amino group (-NH2), and a guanidine group (-NH-C(NH2)-NH2). The carboxyl group is located at one end of the molecule, while the amino group is at the other end. The guanidine group is positioned in the middle of the molecule, connecting the carboxyl and amino groups.
The linear structure of creatine allows it to easily participate in chemical reactions and interactions within the body. This structural arrangement enables creatine to be involved in various biological processes, such as energy metabolism and muscle contraction.
Creatinine
In contrast to creatine, creatinine possesses a heterocyclic structure. It contains a five-membered ring known as an imidazole ring, which is composed of four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom. Attached to the imidazole ring are an amino group (-NH2) and a methyl group (-CH3).
The presence of the heterocyclic imidazole ring in creatinine contributes to its distinct chemical properties and biological functions. This structure allows creatinine to be easily detected and measured in bodily fluids, particularly in urine, making it a valuable marker for assessing kidney function.
The heterocyclic structure of creatinine also affects its solubility and stability, influencing its elimination from the body through the kidneys. Due to its molecular structure, creatinine is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine, providing insights into renal function and overall health.
In summary, while creatine has a linear molecular structure, creatinine possesses a heterocyclic structure with an imidazole ring. These structural differences contribute to their unique characteristics, functions, and roles in various physiological processes.
Creatine vs Creatinine: Molar Mass
Creatine
The molar mass of creatine is 131.13 g/mol. Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule. Creatine has a relatively high molar mass due to its complex structure and the presence of multiple atoms.
To calculate the molar mass of creatine, we add up the atomic masses of its constituent elements. Creatine consists of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) atoms. The atomic masses of these elements are approximately 12.01 g/mol for carbon, 1.01 g/mol for hydrogen, 14.01 g/mol for nitrogen, and 16.00 g/mol for oxygen.
By multiplying the number of atoms of each element in the molecule by their respective atomic masses and summing them up, we arrive at the molar mass of creatine. In this case, the molar mass of creatine is 131.13 g/mol.
Creatinine
The molar mass of creatinine is 113.12 g/mol. Like creatine, creatinine also has a relatively high molar mass due to its complex structure and the presence of multiple atoms.
Creatinine contains carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) atoms. By determining the atomic masses of these elements (approximately 12.01 g/mol for carbon, 1.01 g/mol for hydrogen, 14.01 g/mol for nitrogen, and 16.00 g/mol for oxygen) and calculating the sum of their contributions, we find that the molar mass of creatinine is 113.12 g/mol.
The molar mass of a compound provides useful information for various applications, such as determining the amount of substance present in a given sample, performing stoichiometric calculations, and understanding the properties and behavior of the compound on a molecular level.
Read Also: Can You Take Creatine Before Bed?
Similarities Between Creatine and Creatinine
Till now we’ve just explored the differences but there are also lots of similarities between Creatine and Crwatinine. Let’s check them below.
Natural Formation
Both creatine and creatinine are naturally formed in the body. They are part of the body’s metabolic processes and play important roles in various physiological functions.
Presence in Blood
Both compounds can be found in the blood. Creatine is synthesized in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas and then transported through the bloodstream to the muscles and brain. Creatinine, on the other hand, is produced from the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells and is also transported through the bloodstream.
Derived from Proteins
Both creatine and creatinine are derived from proteins. Creatine is synthesized from the amino acids glycine, L-arginine, and L-methionine, while creatinine is formed by the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells.
Excretion through Kidneys
Both compounds are eliminated from the body through the kidneys. Creatine is converted into creatinine, which is then filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine. Measuring creatinine levels in the blood and urine is commonly used to assess kidney function.
Importance in Exercise Performance
Both creatine and creatinine have implications for exercise performance. Creatine supplementation is popular among athletes and bodybuilders due to its potential to enhance muscle strength and power output. Creatinine levels can also be affected by exercise and physical activity, reflecting changes in muscle metabolism.
Metabolic Homeostasis
Both creatine and creatinine are involved in maintaining metabolic homeostasis in the body. They are part of the complex network of biochemical reactions that regulate energy production, muscle function, and waste product elimination.
How Much Can Creatine Raise Creatinine Levels?
Studies have generally observed only a minor rise in creatinine levels, even when individuals consume doses of around 20 grams per day.
Again, a single instance of acute renal failure was documented in a 20-year-old man who consumed 20 grams of creatine daily for four weeks. In general, doses of 5 grams per day or lower are not expected to significantly elevate creatinine levels in healthy adults.
However, higher doses of creatine may potentially result in a false positive for elevated creatinine levels.
Creatine vs Creatinine in Urine
Creatine and creatinine are both related compounds that play different roles in the body, particularly in relation to urine production. Here’s an analysis of creatine and creatinine in urine:
Creatine in Urine
Creatine is a naturally occurring substance found in the body, primarily in muscles, where it serves as an energy source for muscle contractions. When creatine is metabolized, a small portion of it breaks down into creatinine, which is considered a waste product. Creatinine is then filtered out of the blood by the kidneys and excreted from the body through urine. The presence of creatine in urine is not typically assessed since its levels are relatively low compared to creatinine.
Creatinine in Urine
Creatinine is the primary waste product resulting from the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells. It is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine, making it a reliable indicator of kidney function. Creatinine levels in urine can be measured, but it is more commonly tested in blood samples.
Read More: Does Creatine Make You Fat?
Creatine vs Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine is a naturally synthesized molecule primarily produced by the liver using amino acids. While creatine monohydrate consists of one molecule of crystalline water bonded to each creatine molecule, creatine hydrochloride replaces the water molecule with hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Are Creatine and Creatinine the same?
No, creatine and creatinine are not the same thing. Creatine is a naturally synthesized molecule primarily produced by the liver using amino acids. While creatine monohydrate consists of one molecule of crystalline water bonded to each creatine molecule, creatine hydrochloride replaces the water molecule with hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Does Creatine Increase Testosterone?
While creatine supplementation has been found to improve exercise performance, multiple studies indicate that it does not have a significant impact on testosterone levels.
If you have concerns about maintaining optimal testosterone levels, it is important to focus on other factors. Ensuring an adequate amount of sleep, engaging in regular exercise, consuming enough calories, and obtaining sufficient levels of vitamin D, magnesium, and zinc are all crucial for maintaining testosterone levels.
Choosing Between Creatine And Carnitine
Consider your personal fitness goals, exercise routine, and intensity when choosing between creatine and carnitine supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best option for you and be aware of any potential side effects before starting any new supplement regimen.
Personal Goals And Preferences
Your personal goals and preferences play a crucial role in determining which pre-workout supplement, Carnitine or Creatine, is right for you. If your primary objective is to enhance fat metabolism and increase energy production during workouts, then Carnitine may be the better choice.
On the other hand, if you’re aiming to improve muscle strength and mass, boost sprint performance, and accelerate post-workout recovery, Creatine could be the ideal option. It’s important to consider your exercise routine and intensity as well when making this decision.
Keep in mind that consulting with a healthcare professional can provide valuable insight tailored to your specific needs. Choose what aligns best with your goals – whether it’s maximizing endurance or building muscle – so you can optimize your workout results.
Exercise Routine And Intensity
Your exercise routine and intensity play a crucial role in determining which pre-workout supplement, either carnitine or creatine, is most suitable for you. If you engage in high-intensity workouts or resistance training, mixing carnitine monohydrate with pure supplements can help improve your performance.
On the other hand, if your focus is on maximizing muscle mass and strength adaptations, enhancing sprint performance, or benefiting from increased aerobic threshold, then creatine supplementation may be more beneficial for you.
Understanding the demands of your exercise routine and the level of intensity involved will guide you towards making an informed decision on which supplement best aligns with your fitness goals.
Potential Side Effects
It is important to note that both creatine and carnitine supplements are generally safe for most individuals when taken in recommended dosages. However, it is crucial to be aware of potential side effects.
Creatine supplementation may cause mild gastrointestinal issues such as stomach cramps or diarrhea in some people, although these side effects are not common. It is also essential to stay hydrated when taking creatine to prevent any possible dehydration.
On the other hand, carnitine supplementation usually does not cause significant side effects but may lead to mild digestive discomfort or nausea in rare cases. As always, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness for your specific needs and circumstances.
Consulting With a Healthcare Professional
It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, including creatine or carnitine. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into whether these supplements are suitable for your specific needs and goals.
They can also assess any potential risks or interactions with existing medications or medical conditions you may have.
Since everyone’s body is unique, it’s important to gather personalized advice before making any decisions about pre-workout supplementation. Your healthcare professional will take into account factors such as your exercise routine, current health status, and personal goals to guide you toward the best choice for you.
Conclusion
After reading the article on creatine vs creatinine I think you’re clear that they are not the same thing. Despite their close relationship, they serve distinct roles and possess unique characteristics.
Hopefully, now you’ve no more confusion. That’s it for now, GoodBye!