Understanding the nuances of legal representation is crucial, especially when dealing with sensitive matters like civil rights cases.
This article delves into the distinctions between an attorney or lawyer civil rights representation differences, shedding light on their roles, responsibilities, and the importance of choosing the right representation for your case.
The choice between an attorney or lawyer civil rights representation differences can significantly impact the outcome of civil rights cases.
By exploring these differences, you’ll be better equipped to make an informed decision that aligns with your needs.
What is an Attorney?
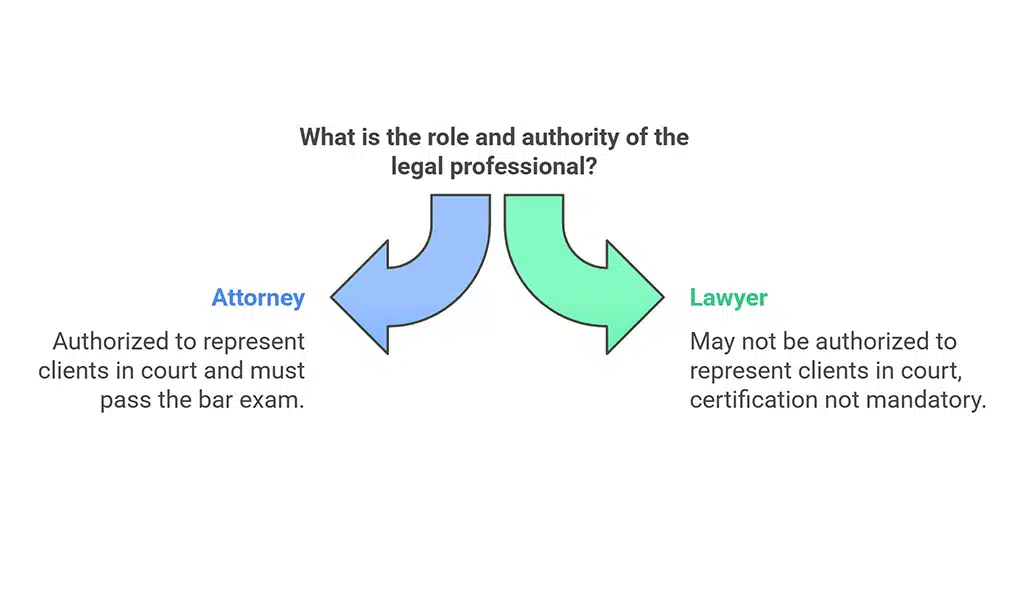
An attorney is a legally qualified professional authorized to represent clients in court. Unlike a generic “lawyer,” an attorney must pass the bar exam in their jurisdiction to practice law formally.
Their role goes beyond giving advice—they can represent clients in legal proceedings, negotiate settlements, and draft critical legal documents.
Attorneys often work within specific legal domains, including civil rights law, where their expertise is indispensable in ensuring justice.
Quick Overview of Attorney Qualifications:
- Holds a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree.
- Passed the bar exam in their practicing jurisdiction.
- Legally authorized to represent clients in court.
Responsibilities of an Attorney in Civil Rights Cases
Attorneys play a pivotal role in civil rights cases. They:
- Represent clients in court, advocating for justice.
- Provide expert legal advice tailored to civil rights issues.
- Draft and review legal documents like complaints, motions, and briefs.
- Negotiate settlements in discrimination or rights violation cases.
Example: In landmark civil rights cases like Brown v. Board of Education, attorneys fought for the desegregation of public schools, showcasing the impact of skilled legal advocacy.
Today, attorneys continue to handle similar issues, such as defending individuals against workplace discrimination or advocating for policy changes to protect marginalized groups.
| Key Roles of Attorneys in Civil Rights Cases | Description |
| Court Representation | Advocates for clients in civil rights trials. |
| Legal Documentation | Prepares complaints, motions, and legal briefs. |
| Negotiation | Mediates settlements in discrimination cases. |
| Policy Advocacy | Helps shape laws impacting civil rights. |
| Benefits of Hiring an Attorney | Why It Matters |
| Expertise in Court Representation | Ensures your case is professionally presented in court. |
| Detailed Legal Knowledge | Provides insights tailored to complex civil rights issues. |
| Strategic Negotiation Skills | It helps secure favorable outcomes outside of court. |
What is a Lawyer?
A lawyer is a broader term encompassing anyone who has attended law school and earned a law degree (Juris Doctor).
However, not all lawyers are authorized to practice law in court. Some may work in academic, advisory, or corporate roles without becoming licensed attorneys.
Lawyers often specialize in legal research, policy analysis, and community education, contributing to the larger legal ecosystem.
Quick Overview of Lawyer Qualifications:
- Holds a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree.
- May or may not be licensed to practice in court.
- Often focuses on advisory, research, or non-litigious roles.
Roles of a Lawyer in Civil Rights Representation
Lawyers can contribute significantly to civil rights advocacy by:
- Conducting thorough legal research and analysis to support cases.
- Advising on non-litigious civil rights matters, such as policy drafting or community education.
- Supporting attorneys in court by preparing documents or strategizing legal arguments.
- Engaging in public advocacy to raise awareness of systemic injustices.
Scenario: A lawyer may work behind the scenes to craft arguments or research precedents for a civil rights case handled by an attorney.
For example, in addressing housing discrimination, a lawyer might analyze historical patterns of zoning laws to support a court argument.
| Key Contributions of Lawyers | Details |
| Legal Research | Provides case precedents and detailed analysis. |
| Community Advocacy | Educates the public on civil rights issues. |
| Policy Drafting | Crafts legislation to protect marginalized groups. |
| Benefits of Consulting a Lawyer | Why It Matters |
| Affordable Advisory Services | Offers cost-effective guidance for simple cases. |
| Policy and Research Expertise | Provides in-depth analysis to strengthen cases. |
| Public Education Initiatives | Helps communities understand their civil rights. |
Key Differences Between Attorneys and Lawyers in Civil Rights Cases
| Criteria | Attorney | Lawyer |
| Education | Law degree (J.D.) | Law degree (J.D.) |
| Certification | Must pass the bar exam | Not mandatory |
| Court Representation | Authorized | Not always authorized |
Scope of Practice
- Attorneys: Handle court cases, represent clients, and provide comprehensive legal counsel.
- Lawyers: May focus on advisory or academic roles without appearing in court. Lawyers often engage in non-litigious activities, such as drafting impactful legal articles or conducting seminars on civil rights awareness.
Interaction with Clients
Attorneys enjoy attorney-client privilege, ensuring confidentiality in legal matters.
Lawyers, depending on their role, may not always operate under this privilege, particularly in non-representative capacities.
| Key Distinction | Attorney | Lawyer |
| Courtroom Expertise | Licensed to represent clients in legal trials. | Limited to advisory roles if not licensed. |
| Confidentiality | Privileged communication under legal codes. | May not always apply to non-attorney lawyers. |
| Focus | Litigation and representation. | Research, policy, and education. |
Choosing the Right Representation for Civil Rights Cases
Factors to Consider
When selecting between an attorney or lawyer civil rights representation differences, consider:
- Nature of the case: Is court representation required, or do you need legal advice?
- Budget: Attorneys often charge higher fees due to their qualifications and responsibilities.
- Complexity: Cases involving litigation typically demand an attorney.
- Urgency: Immediate legal action often necessitates hiring an attorney.
When to Hire an Attorney
You should hire an attorney when:
- Your case involves litigation or court appearances.
- Legal documents need formal drafting and filing.
- You seek representation in high-stakes civil rights cases, such as discrimination lawsuits.
Case Example: A victim of workplace discrimination might require an attorney to file a lawsuit and represent them in court.
Attorneys also play a critical role in cases involving constitutional rights violations, such as unlawful surveillance or suppression of free speech.
| Situations Requiring an Attorney | Examples |
| Litigation | Courtroom representation for discrimination. |
| Complex Legal Documents | Drafting and filing legal briefs. |
| High-Stakes Advocacy | Fighting systemic policy injustices. |
| Urgent Legal Actions | Injunctions to prevent immediate harm. |
When a Lawyer May Be Sufficient
A lawyer may be adequate for:
- Advisory roles, such as understanding your civil rights.
- Community-level advocacy or educational campaigns.
- Non-litigious cases.
Scenario: Consulting a lawyer for guidance on filing a discrimination complaint with the EEOC or navigating workplace policies that may infringe on your civil rights.
| Situations Suited for Lawyers | Examples |
| Advisory Roles | Providing insight on civil rights laws. |
| Community Education | Hosting seminars on rights awareness. |
| Non-Court Advocacy | Drafting policies to improve workplace equity. |
Common Misconceptions About Attorneys and Lawyers
Myths About Legal Titles
- “All attorneys are lawyers”: While all attorneys are lawyers, not all lawyers qualify as attorneys.
- “Only attorneys understand civil rights laws”: Lawyers, especially those specializing in civil rights, can provide substantial insights.
- “Lawyers can never represent clients in court”: Some lawyers, if licensed, may represent clients in specific jurisdictions.
Clarifying Civil Rights Representation
Misunderstandings often arise around who can best represent civil rights cases.
Attorneys are indispensable for courtroom advocacy, while lawyers can be instrumental in research, policy advising, and community outreach.
| Common Misconceptions | Reality |
| Only attorneys can help. | Lawyers provide essential support in many areas. |
| Lawyers lack expertise. | Many lawyers specialize in civil rights issues. |
| Attorneys are the same. | Attorneys are lawyers with court certification. |
Takeaways
Understanding attorney or lawyer civil rights representation differences is critical for effectively navigating civil rights cases.
While attorneys can represent you in court, lawyers provide valuable support in advisory roles.
Evaluate your legal representation needs carefully. Consult online resources or reach out to legal directories to find the right professional for your civil rights case.
Take the first step toward justice by choosing the representation that aligns with your needs.